tags : Spring Boot
It was developed by Rod Johnson in 2003. Spring framework makes the easy development of JavaEE application.
It can be thought of as a framework of frameworks because it provides support to various frameworks such as Struts, Hibernate, Tapestry, EJB, JSF, etc.
The Spring framework comprises several modules such as IOC, AOP, DAO, Context, ORM, WEB MVC etc
what is a framework?
A framework is like a structure that provides a foundation for the application development process.
- A framework acts as a template that developers can use to avoid writing everything from scratch.
- It provides a set of tools and elements that facilitate speedy development.
Inversion of Control is a key part of what makes a framework different to a library. A library is essentially a set of functions that you can call, these days usually organized into classes. Each call does some work and returns control to the client. But frameworks controls the flow and decides when to call a function.
Advantages of Spring Framework
1) Predefined Templates
Spring framework provides templates for JDBC, Hibernate, JPA etc. technologies. So there is no need to write too much code. It hides the basic steps of these technologies.
Let’s take the example of JdbcTemplate, you don’t need to write the code for exception handling, creating connection, creating statement, committing transaction, closing connection etc. You need to write the code of executing query only. Thus, it save a lot of JDBC code.
2) Loose Coupling
The Spring applications are loosely coupled because of dependency injection.
3) Easy to test
The Dependency Injection makes easier to test the application. The EJB or Struts application require server to run the application but Spring framework doesn’t require server.
4) Lightweight
Spring framework is lightweight because of its POJO implementation. The Spring Framework doesn’t force the programmer to inherit any class or implement any interface. That is why it is said non-invasive.
5) Fast Development
The Dependency Injection feature of Spring Framework and it support to various frameworks makes the easy development of JavaEE application.
6) Powerful abstraction
It provides powerful abstraction to JavaEE specifications such as JMS, JDBC, JPA and JTA.
7) Declarative support
It provides declarative support for caching, validation, transactions and formatting.
Spring Modules
The Spring framework comprises of many modules such as core, beans, context, expression language, AOP, Aspects, Instrumentation, JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS, Transaction, Web, Servlet, Struts etc. These modules are grouped into Test, Core Container, AOP, Aspects, Instrumentation, Data Access / Integration, Web (MVC / Remoting) as displayed in the following diagram.
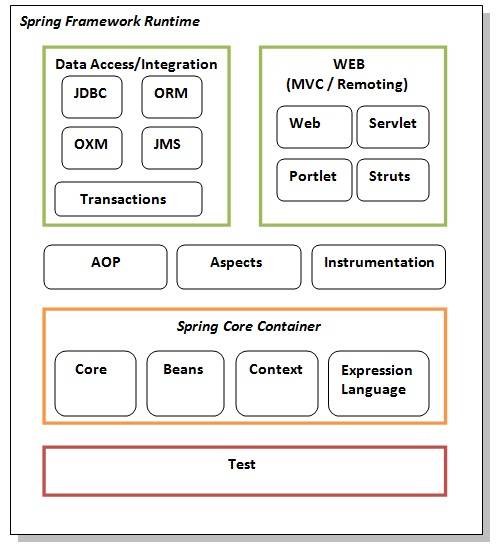
Test
This layer provides support of testing with JUnit and TestNG.
Spring Core Container
The Spring Core container contains core, beans, context and expression language (EL) modules.
Core and Beans
These modules provide IOC and Dependency Injection features.
Context
This module supports internationalization (I18N), EJB, JMS, Basic Remoting.
Expression Language
It is an extension to the EL defined in JSP. It provides support to setting and getting property values, method invocation, accessing collections and indexers, named variables, logical and arithmetic operators, retrieval of objects by name etc.
AOP, Aspects and Instrumentation
These modules support aspect oriented programming implementation where you can use Advices, Pointcuts etc. to decouple the code.
The aspects module provides support to integration with AspectJ. The instrumentation module provides support to class instrumentation and classloader implementations.
Data Access / Integration
This group comprises of JDBC, ORM, OXM, JMS and Transaction modules. These modules basically provide support to interact with the database.
Web
This group comprises of Web, Web-Servlet, Web-Struts and Web-Portlet. These modules provide support to create web application.