tags : Algorithms, Collection
What is Hashing
 It is the process of converting an object into an integer value. The integer value helps in indexing and faster searches.
It is the process of converting an object into an integer value. The integer value helps in indexing and faster searches.
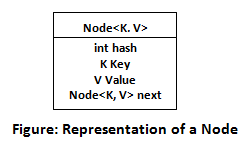
HashMap contains an array of the nodes, and the node is represented as a class. It uses an array and LinkedList data structure internally for storing Key and Value. There are four fields in HashM
Equals vs HashCode
-
equals(): It checks the equality of two objects. It compares the Key, whether they are equal or not. It is a method of the Object class. It can be overridden. If you override the equals() method, then it is mandatory to override the hashCode() method.
-
hashCode(): This is the method of the object class. It returns the memory reference of the object in integer form. The value received from the method is used as the bucket number. The bucket number is the address of the element inside the map. Hash code of null Key is 0.
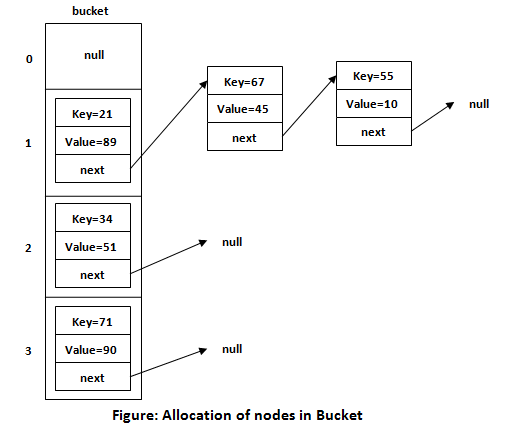
Buckets
Array of the node is called buckets. Each node has a data structure like a LinkedList. More than one node can share the same bucket.
Example
In the following example, we want to insert three (Key, Value) pair in the HashMap.
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Aman", 19);
map.put("Sunny", 29);
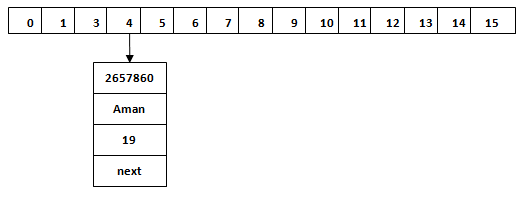
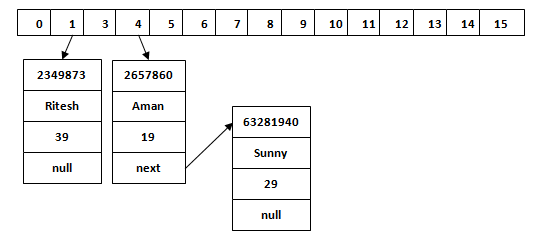
map.put("Ritesh", 39); When we call the put() method, then it calculates the hash code of the Key “Aman.” Suppose the hash code of “Aman” is 2657860. To store the Key in memory, we have to calculate the index.
Calculating Index
Index minimizes the size of the array. The Formula for calculating the index is:
Index = hashcode(Key) & (n-1) Where n is the size of the array. Hence the index value for “Aman” is:
Index = 2657860 & (16-1) = 4 The value 4 is the computed index value where the Key and value will store in HashMap.
Hash Collision
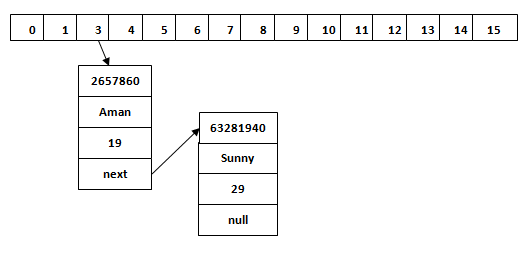
This is the case when the calculated index value is the same for two or more Keys. Let’s calculate the hash code for another Key “Sunny.” Suppose the hash code for “Sunny” is 63281940. To store the Key in the memory, we have to calculate index by using the index formula.
Index=63281940 & (16-1) = 4
The value 4 is the computed index value where the Key will be stored in HashMap. In this case, equals() method check that both Keys are equal or not. If Keys are same, replace the value with the current value. Otherwise, connect this node object to the existing node object through the LinkedList. Hence both Keys will be stored at index 4.
Similarly, we will store the Key “Ritesh.” Suppose hash code for the Key is 2349873. The index value will be 1. Hence this Key will be stored at index 1.
get() method in HashMap
get() method is used to get the value by its Key. It will not fetch the value if you don’t know the Key. When get(K Key) method is called, it calculates the hash code of the Key.
map.get(new Key("Aman"));- It generates the hash code and calculates the index value by using index formula.
- get() method then searches for the index value 4.
- It compares the first element Key with the given Key.
- If both keys are equal,
- then it returns the value
- else check for the next element in the node if it exists.
- It returns null if the next of the node is null.